A Guide To The Different Types Of Birth Control + Choosing The Best One For You
The Different Types Of Birth Control
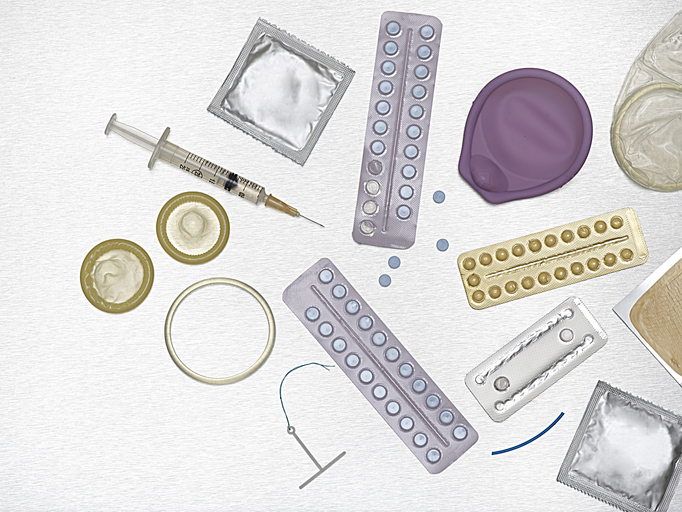
Source: SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty
Hormonal
The Shot
Best For: The Forgetful
What you might pay: Depending on insurance, $0 and up to $150 per shot
Remembering to take a birth control pill every single day, let alone pack your pills, isn’t for everyone. And if you rely on condoms, you’ll have to make sure you have those stashed away in the appropriate places. If you worry you won’t remember these methods, then the shot could be for you.
The depo provera shot involves an injection that you’ll receive from your doctor, every three months. So all you have to do is remember to make that appointment every 90 days. The shot itself contains the hormone progestin, which stops ovulation from taking place.
It can be 99 percent effective when taken properly. Most see effectiveness of 94 percent.
The Birth Control Pill
Best for: The Skittish
What you might pay: Depending on insurance, $0 to $50 per month
On this list, we’ll go over shots, surgically implanted items, surgeries and more invasive options. But for those who don’t like needles, stirrups or anything that feels invasive, the pill is a great, simple option. You probably already take other medications, as well as supplements, so swallowing a tiny pill will feel natural.
There are three types of pills: the combination pill, the progestin-only pill and the continuous use pill.
The combination pill contains estrogen and progestin. It prevents pregnancy in two ways: first, it stops ovulation. Then, it thickens the fluid around your cervix, making it more difficult for sperm to make it to the uterus.
Progestin-only pills primarily prevent pregnancy by thickening the fluid around the cervix, as well as thinning the lining of the uterus. This makes it difficult for sperm to reach the uterus, and for an egg to implant. Some progestin-only pills also stop ovulation.
Continuous use pills are those you take for anywhere from 12 to 84 days without a break, according to Mayo Clinic. With the combination and progestin-only pills, you take active pills for three weeks, and then one week of placebo pills.But with continuous use pills, you will not take placebo pills for an extended period of time. This means you skip your period for a while which, for some women with certain conditions like painful periods, can be a benefit.
These pills can offer 99 percent effectiveness with perfect use and between 91 to 93 percent with typical use.
The Patch
Best for: The Forgetful + Needle-Averse
What you might pay: Depending on insurance, $0 to $150 per month
Some women worry they won’t remember to take the pill every day, but also have a fear of needles. The transdermal patch can be a great option. You will need to replace your patch once a week.
The patch is placed on your butt, back or arm. It releases estrogen and progestin – the same hormones found in the pill – into your body, stopping ovulation. Much like with the combination and progestin-only pills, there is a one week break from hormones. You apply a new patch every week, for three weeks, then do one patch-free week, and restart the cycle.
With perfect use it can be 99 percent effective and with typical use is 91 percent effective.
The Ring
Best for: The Discreet
What you might pay: Depending on insurance, $0 to $200 per month
The vaginal ring is a two-inch-wide plastic ring that you place inside of yourself. It releases estrogen and progesterone and stops ovulation. You leave each ring in for three weeks, remove it for a one-week break, and then put in a new one.
The ring is 99 percent effective with perfect use and 91 percent effective with typical use.
Hormonal IUD
Best for Prolonged Prevention
What you might pay: Depending on insurance, $0 to $1,300 every three to eight years depending on the brand.
The hormonal IUD is good for people who don’t want to birth for several years – three to eight to be exact. This is a small device that your doctor implants in your uterus. It releases progestin, stopping ovulation, and can remain there for several years at a time.
The hormonal IUD is one of the most effective forms of birth control, at over 99 percent effective.









